
However, the last Rajah of Sarawak, Sir Charles Vyner Brooke decided to cede Sarawak as part of British Crown Colony in 1946. The Japanese government set up a Batu Lintang camp near Kuching to hold prisoners of war and civilian internees. During World War II, Kuching was occupied by Japanese forces from 1942 to 1945.
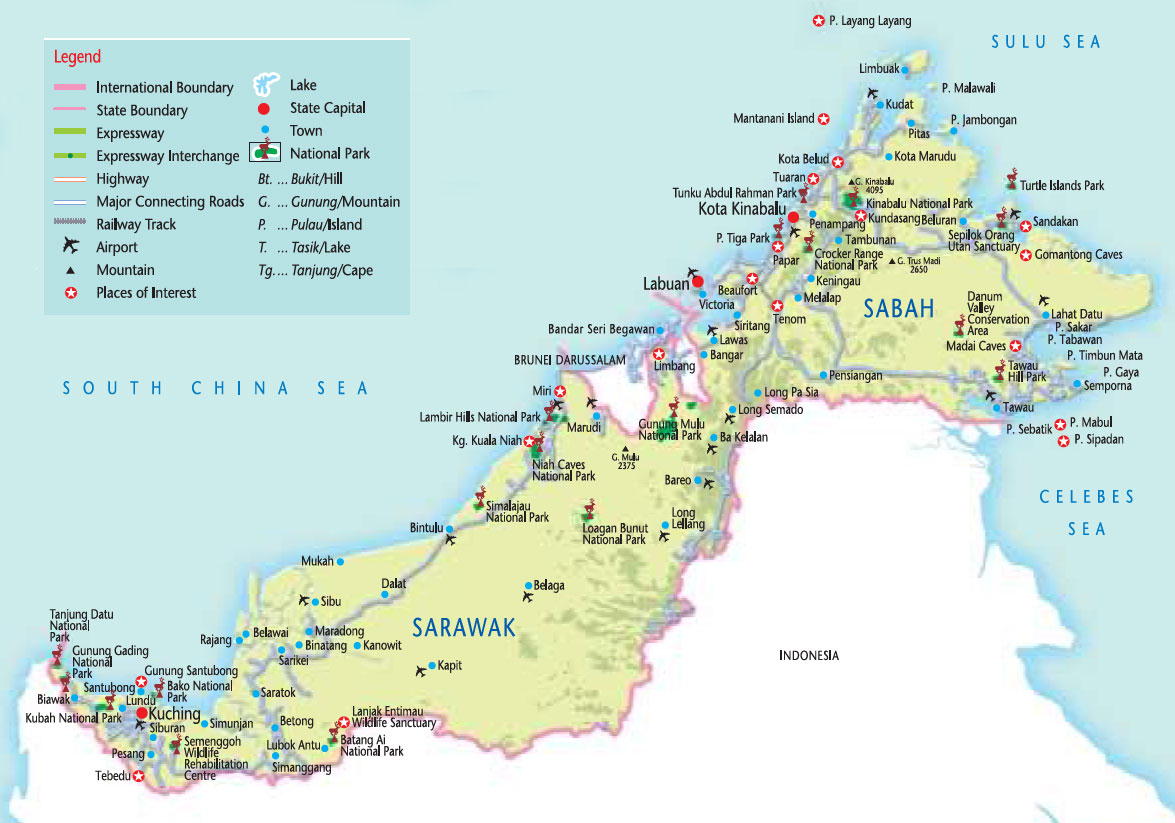
In 1941, the Brooke administration had a Centenary Celebration in Kuching. The town continued to receive attention and development during the rule of Charles Brooke such as the construction of a sanitation system, hospital, prison, fort, and a bazaar. In 1841, Kuching became the capital of the Kingdom of Sarawak after the territory in the area was ceded to James Brooke for helping the Bruneian empire in crushing a rebellion particularly by the interior Borneo dwelling Land Dayak people who later became his loyal followers after most of them were pardoned by him and joined his side. Kuching was the third capital of Sarawak in 1827 during the administration of the Bruneian Empire. The city is on the Sarawak River at the southwest tip of the state of Sarawak on the island of Borneo and covers an area of 431 km 2 (166 sq mi) with a population about 165,642 in the Kuching North administrative region and 159,490 in the Kuching South administrative region -a total of 325,132 people. It is also the capital of Kuching Division. Kuching ( / ˈ k uː tʃ ɪ ŋ/), officially the City of Kuching, is the capital and the most populous city in the state of Sarawak in Malaysia. QA and QK (for all vehicles except taxis)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
